- grandMA2 User Manual
- New in the Manual
- Introduction
- About this manual
- System requirements grandMA2 onPC
- Installation of grandMA2 onPC
- Help from MA technical support
- Safety Information
- Symbols used
- Intended use
- Dangers caused by electric current
- General safety instructions
- Device Overview
- grandMA2 console
- grandMA2 replay unit (RPU)
- grandMA2 fader wing
- MA onPC command wing
- MA onPC fader wing
- System Overview
- Standalone systems
- Network systems
- What is the replay unit (RPU)
- What is the network processing unit (NPU)
- What is the MA video processing unit (VPU)
- What is the network dimmer processor (NDP)
- What is MA 3D
- What are the MA nodes
- Paramters vs. DMX channels
- Parameter expansion
- Big systems
- Media systems and CITP
- First Steps
- Unpack the device
- Check scope of delivery
- Position the device
- Connect power
- Connect desk lamps
- Connect external screens
- Connect USB mouse and USB keyboad
- Connect DMX
- Connect sound
- Connect SMPTE (LTC)
- Connect Ethernet
- Connect analog remote control
- Connect grandMA2 fader wing
- Setup your PC
- Turn on the console the first time
- Keys & Buttons on the Console
- Key overview
- >>> [GoFastForward]
- <<< [GoFastBack]
- . [Dot]
- Align
- Assign
- At
- Backg [Background]
- Backup
- Blind
- Bt Pg +
- Bt Pg -
- B.O. [Blackout]
- Channel
- Ch Pg +
- Ch Pg -
- Clear
- Copy
- Cue
- Del [Delete]
- Down
- Edit
- Effect
- [Encoder]
- Esc
- Exec [Executor]
- Executor Buttons
- Fd Pg +
- Fd Pg -
- Fix
- Fixture
- Freeze
- Full
- Go + [small]
- Go + [large]
- Go - [small]
- Go - [large]
- Goto
- Group
- Help
- Highlt [Highlight]
- If
- Keyboard
- Learn
- List
- MA
- Macro
- [Minus] -
- Mouse
- Move
- Next
- [Numeric]
- Off
- On
- Oops
- Page
- Pause [small]
- Pause [large]
- Please
- [Plus] +
- Preset
- Prev [Previous]
- Prvw [Preview]
- Select
- Sequ [Sequence]
- Set
- Setup
- Solo
- Store
- Temp
- Thru
- Time
- Top
- Tools
- Up
- Update
- User 1
- User 2
- View
- U1 - U4
- V1 - V10
- X1 - X20
- Workspace
- User interface
- Screen layout
- User-defined area
- Command line
- X-Key labels
- View buttons
- Master section
- Time control
- Encoder bar
- Preset control bar
- Encoder toolbar
- Encoder settings
- Command wing bar
- Command section
- Mini executor bar
- Work with views
- Touch gestures
- Calculator
- Info
- Oops and undo
- Colors
- System
- Marker
- Cue
- Text indicators and symbols
- Icons
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Turn on or turn off the keyboard shortcuts
- Edit keyboard shortcuts
- Add or delete keyboard shortcuts
- Export or import keyboard shortcuts
- User interface
- Windows in General
- Create and manage basic windows
- Clear the screen or delete windows
- Command Syntax and Keywords
- General syntax rules
- Helping keywords
- Object keywords
- Function keywords
- All keywords
- Special characters
- <<< [GoFastBack]
- >>> [GoFastForward]
- - [Minus]
- + [Plus]
- AddUserVar
- AddVar
- Agenda
- Alert
- Align
- AlignFaderModules
- All
- AllButtonExecutors
- AllChaseExecutors
- AllFaderExecutors
- AllRows
- AllSequExecutors
- And
- Appearance
- Asterisk *
- Assign
- At
- At @
- Attribute
- AutoCreate
- Backup
- Black
- Blackout
- BlackScreen
- Blind
- BlindEdit
- Block
- ButtonPage
- Call
- Camera
- ChangeDest
- Channel
- ChannelFader
- ChannelLink
- ChannelPage
- Chat
- CircularCopy
- Clear
- ClearActive
- ClearAll
- ClearSelection
- Clone
- CmdDelay
- CmdHelp
- Copy
- CrashLogCopy
- CrashLogDelete
- CrashLogList
- Crossfade
- CrossfadeA
- CrossfadeB
- Cue
- Cut
- Default
- DefGoBack
- DefGoForward
- DefGoPause
- Delay
- Delete
- DeleteShow
- DisconnectStation
- Dmx
- Dollar $
- DmxUniverse
- Dot .
- DoubleRate
- DoubleSpeed
- Down
- DropControl
- Edit
- Effect
- EffectAttack
- EffectBPM
- EffectDecay
- EffectDelay
- EffectFade
- EffectForm
- EffectHigh
- EffectHZ
- EffectID
- EffectLow
- EffectPhase
- EffectSec
- EffectSpeedGroup
- EffectWidth
- Empty
- EndIf
- EndSession
- Escape
- ExecButton1
- ExecButton2
- ExecButton3
- Executor
- Exit
- Export
- Extract
- Fade
- FadePath
- Fader
- FaderPage
- Feature
- Filter
- Fix
- Fixture
- FixtureType
- Flash
- FlashGo
- FlashOn
- Flip
- Form
- Freeze
- Full
- FullHighlight
- Gel
- Go
- GoBack
- Goto
- Group
- HalfRate
- HalfSpeed
- Help
- Highlight
- IdentifyFaderModule
- If
- IfActive
- IfOutput
- IfProg
- Image
- Import
- Info
- Insert
- Interleave
- Invert
- InviteStation
- Item3D
- JoinSession
- Kill
- Label
- Layer
- Layout
- Learn
- LeaveSession
- List
- ListEffectLibrary
- ListFaderModules
- ListLibrary
- ListMacroLibrary
- ListOops
- ListOwner
- ListPluginLibrary
- ListShows
- ListUpdate
- ListUserVar
- ListVar
- Load
- LoadNext
- LoadPrev
- LoadShow
- Locate
- Lock
- Login
- Logout
- Lua
- Macro
- ManualXFade
- Mask
- Master
- MasterFade
- MAtricks
- MAtricksBlocks
- MAtricksFilter
- MAtricksGroups
- MAtricksInterleave
- MAtricksReset
- MAtricksWings
- MediaServer
- Menu
- Message
- Messages
- MidiControl
- MidiNote
- MidiProgram
- Model
- Move
- Move3D
- NetworkInfo
- NetworkNodeInfo
- NetworkNodeUpdate
- NetworkSpeedTest
- NewShow
- Next
- NextRow
- Normal
- Off
- On
- Oops
- Or
- OutDelay
- OutFade
- Page
- Parentheses ( )
- Park
- Part
- Paste
- Pause
- Plugin
- PMArea
- Preset
- PresetType
- Preview
- PreviewEdit
- PreviewExecutor
- Previous
- PrevRow
- Profile
- Protocol
- PSR
- PSRList
- Quotation marks " "
- PSRPrepare
- Rate
- Rate1
- RdmAutomatch
- RdmAutopatch
- RdmFixtureType
- RdmInfo
- RdmList
- RdmSetParameter
- RdmSetpatch
- RdmUnmatch
- Reboot
- Record
- Release
- ReloadPlugins
- Remote
- RemoteCommand
- Remove
- RemoveIndividuals
- Replace
- ResetDmxSelection
- ResetGuid
- Restart
- Root
- Rotate3D
- SaveShow
- Screen
- Search
- SearchResult
- Select
- SelectDrive
- Selection
- Semicolon ;
- SelFix
- Sequence
- SetHostname
- SetIP
- SetNetworkSpeed
- Setup
- SetUserVar
- SetVar
- ShuffleSelection
- ShuffleValues
- Shutdown
- SnapPercent
- Slash /
- Solo
- SpecialMaster
- Square brackets [ ]
- Speed
- StepFade
- StepInFade
- StepOutFade
- Stomp
- Store
- StoreLook
- Surface
- Swop
- SwopGo
- SwopOn
- SyncEffects
- TakeControl
- Telnet
- Temp
- TempFader
- Thru
- Timecode
- TimecodeSlot
- Timer
- ToFull
- Toggle
- Tools
- Top
- ToZero
- Unblock
- Unlock
- Unpark
- Up
- Update
- UpdateFirmware
- UpdateSoftware
- UpdateThumbnails
- User
- UserProfile
- Value
- Version
- View
- ViewButton
- ViewPage
- WebRemoteProgOnly
- With
- World
- Zero
- Work with lists
- Object list
- Selection list
- Executor list
- Attribute list
- Station list
- General syntax rules
- Using the Backup Menu
- New show
- Load show
- Save show
- Save show as...
- Delete shows
- Using a USB stick
- Setting up a file server
- Partial show read
- ASCII show read
- Save as grandMA3
- Single User and Multi User Systems
- The difference between a single user and a multi user system
- Create user profiles and users
- User settings
- Login
- Networking
- What is networking
- Set the IP address in the console
- Set the IP address in the onPC
- Using DHCP in MA devices
- Session control
- How to create a session
- Protecting the session and station
- Adding devices to the session
- How to end or leave a session
- Session collision
- Getting DMX in and out of the system
- Setting up DMX ports on MA devices
- Network DMX protocols
- What affects my DMX output?
- Using CITP
- Streaming CITP
- Thumbnail exchange
- PosiStageNet (PSN)
- FTP connection to console and NPU
- Patching, DMX, and Fixture Setup
- What are channels & fixtures
- Attributes
- DMX break
- What is 3D and stage setup
- Adding fixtures to the show
- Delete fixtures from the show
- Working with layers
- Multipatching
- Live patching
- DMX sheet
- DMX testing
- DMX and parameter lists
- Universe pool
- Stage view
- Virtual 3D cameras
- Position fixtures in the 3D stage
- Auto calibrate fixture positions
- What are channels & fixtures
- Basic Fixture Types
- What are attributes, features & preset types
- ColorMix vs. MixColor
- Different fixture types
- Conventional
- LED
- Mirror
- Moving lights
- Media server
- Virtual fixtures
- Operate Fixtures
- Channel sheet
- Fixture sheet
- Sheet options
- Tools
- Layer mask
- Display
- Title buttons
- Assign executor
- Mask (local)
- Layers in sheets
- Channel sheet and fixture sheet
- Sequence content and sequence tracking sheet
- What is the programmer
- Encoder grouping
- Using the color picker
- Using the shaper dialog
- Using the smart view
- Edit a channel or fixture
- Pools in General
- Manage pool objects
- Adjust pool options
- Call modes
- Groups
- Create groups
- Auto create groups
- Using groups when programming
- Choose copy method
- Change specific group colors
- Group masters
- Presets
- What are special modes
- Preset pools
- Preset pool "Dynamic"
- Create presets
- Preset pool options
- Create preset reference
- Auto create presets
- Auto create additional presets
- Embedded presets
- Edit presets
- Update presets
- Delete presets
- Cues and Sequences
- What are cues and sequences
- Looking at the cue sequence
- Store cues
- Store options and defaults
- Cue timings
- Renumber cues
- Delete cues
- Playing back cues
- Looking at the cue content
- Update cues
- What is tracking
- What is MIB
- Sequence mini executor
- Commands in cues
- Executors
- What are executors
- Executors on the screens
- Assign a function
- Looking at the active executors
- Common executor options
- Advanced Sequence Functionality
- Using different view sets in the sheets
- Working with MIB
- Using cue modes
- Cue zero
- Sequence info window
- Looping cues
- Cue path
- Advanced Executor Functionality
- Executor pages
- Channel pages
- Executor options
- Masters window
- Special masters
- Default masters
- Grand masters
- Speed masters
- Rate masters
- Playback masters
- Clone
- Clone in user interface
- Examples
- Clone presets
- Search and Replace
- Search
- Replace
- Image Pool
- Import images and videos
- Image limitations & guidelines for symbols
- Supported file formats
- Delete images and videos
- Layouts
- Create a layout
- Layout pool options
- Edit layout
- Layout view options
- Worlds, Filters and Masks
- What are worlds
- Create worlds
- Auto create worlds
- Use worlds when programming
- What are filters
- Create filters
- Use filters when programming
- Use temporary filters
- What are masks
- Create masks
- Use masks in the sheets
- Apply worlds or filters to executors and sequences
- MAtricks
- MAtricks toolbar
- MAtricks pool
- MAtricks interleave
- MAtricks blocks
- MAtricks wings
- MAtricks groups
- Chasers
- Create a chaser
- Chaser settings
- Chaser mini executor
- Effects
- Use predefined effects
- Use template and selective effects
- Create an effect in the programmer
- Create an effect that uses presets
- Create effect forms
- Pool options
- Effects in a cue
- Assign effect to executor
- Live edit an effect
- Running effects
- Update effects
- Delete effects
- Bitmap Fixture
- Import bitmap fixture
- Apply bitmap fixture in the layout
- Control bitmap fixture
- Edit bitmap fixture
- Example
- Priorities for bitmap effects
- Disable bitmap for fixtures
- XYZ
- XYZ vs. pan/tilt
- XYZ and pan/tilt in cues and sequences
- Use stage markers
- Link objects to stage markers in MA 3D
- Remote Controlling the System
- Remote input
- MIDI show control (MSC)
- Web remote
- Telnet remote
- Decimal – hex table
- Timecode
- What is timecode and timecode shows
- Record a timecode show
- Edit a timecode show
- Playing back a timecode show
- Organize the show with multiple timecode shows
- Timer
- Timer pool
- Timer pool options
- Agenda
- What is agenda
- Create an appointment in the agenda
- Macros
- What are macros
- Manually create a macro
- Use variables
- Create pop-ups
- Conditional expressions
- Macro timing
- Record a macro
- Edit a macro
- Command line interaction
- Assign a macro to a key
- Example macros
- Plugins
- What is Lua
- Edit plugins
- Partial Show Read
- What is partial show read (PSR)
- How to do a PSR
- RDM
- Turn RDM on
- Match RDM devices
- Auto patch RDM devices
- Work with RDM parameters
- Work with RDM sensors
- Configure RDM notifications
- Use the RDM sheet
- Unmatch RDM devices
- Splitters and mergers that support RDM
- Turn RDM off
- RDM specific keywords
- DMX Profiles
- Other System Tools
- Message center
- Help
- Clock
- Sound input window
- VPU pixel mapper view
- Network dimmer
- Views
- Errors
- Readout
- Edit properties of a rack
- Edit a module
- Desk status
- Performance window
- System monitor
- Export and Import
- Export by using command line
- Export by using user interface
- Import by using command line
- Import by using user interface
- Import predefined objects
- Update the Software
- Update via setup
- Format a USB stick for Linux
- Update or factory reset via boot menu
- Restart from Linux
- Advanced Fixture Types
- Anatomy of a fixture type
- Module manager
- Instance manager
- Wheel manager
- Attribute & Encoder Grouping
- Anatomy of a fixture type
- grandMA2 onPC Details
- Control the MA NDPs
- Add the MA NDPs
- Configure the MA NDPs
- Delete the MA NDPs
- Control the MA Network Switch
- Add MA Network Switch
- Change IP address
- Enable DHCP client
- Change hostname
- Change switch ID
- Configure ports
- Edit groups
- Edit presets
- Edit LAGs
- Mirror ports
- Work with the switch configuration
- Disable SNMP
- Change password
- Update firmware
- Reset to factory defaults
- Delete MA Network Switch
- Control the MA xPort Nodes
- Add the MA xPort Nodes
- Configure the MA xPort Nodes in the console
- Configure the MA xPort Nodes in a browser
- Configure the MA xPort Nodes as splitters or mergers
- Delete the MA xPort Nodes
- Console Settings
- Adjust the intensity of desk lights
- Change screen options
- Local settings
- Wing & monitor setup
- Date & time
- Shut Down the System
- Error Messages
- Technical Data
- Glossary
- grandMA3 Mode2
- grandMA2 Quick Start Guide
- grandMA2 Quick Manual onPC solutions
- MA 3D
- MA VPU
- Release Notes
New help version
The help version you selected belongs to an older software version. You may want to view the latest help version.
MIDI Show Control (MSC)
Table of contents of this topic
MIDI Show Control (MSC) is a different way to remote control the system.
It was released in 1991 as an extension to the MIDI protocol. The grandMA2 system is capable of receiving and transmitting MSC.
There are a lot of settings to MSC. Most of these are setting to be able to match the transmitting and receiving devices. Please read below.
Below the settings there is a description of the MSC concept and then some words about transporting MIDI using Ethernet.
Setting up MSC
To access these settings, press the Setup key and then the Midi Show Control button under the Console tab.
The settings could look like this:
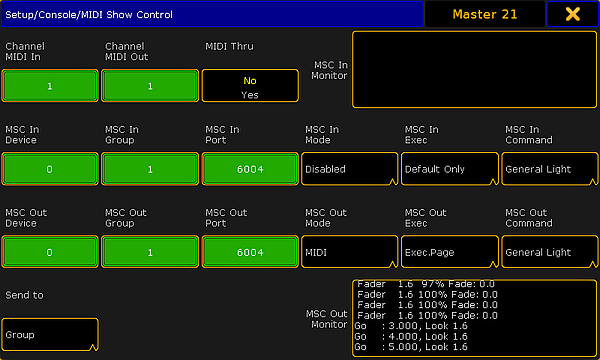
There are four rows with different settings and two monitor fields.
The monitor fields display the incoming and outgoing MSC. They display the data as interpreted data, meaning that it does not show the raw hex data.
The top row has two input fields and one toggle button:
- Channel MIDI In:
There are 16 different channels in MIDI. The number in the In field needs to match the channel number from the transmitter. - Channel MIDI Out:
The channel number in this field need to match the channel number of the MSC receiver. - MIDI Thru:
This toggle button turn On or Off is any incoming MIDI should also be sent out of the MIDI output.
If MSC commands are transmitted and received on the same MIDI channel, then a loop will be created.
The next two lines are the same except the first is the settings for any incoming MSC and the second is the outgoing MSC.
- Device:
There are 112 different devices in MSC. MSC also specifies an "All" option. This is set in the Send to button at the lower left corner - read about it below. This input accepts values from 0 to 111. - Group:
The MSC standard has the option to organize the devices in 15 different groups. Here it is possible to set a group number from 1 to 15. Please read about the Send to setting below. - Port:
If MSC is to be sent using an Ethernet connection, then there needs to be an IP port number. This can be set here. The default number is 6004. The port number needs to be between 6000 and 6100. - Mode:
Tapping here opens a Select MSC Mode pop-up: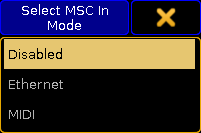
Select MSC (In) Mode pop-up
There are three options here:- Disabled - this is the same turning off the MSC input or output.
- Ethernet - This will use MSC via Ethernet - Please read more about MSC via Ethernet below.
- MIDI - This will use the MIDI ports on the station to transmit or receive MSC.
- Exec:
Tapping here opens the Select MSC Exec pop-up: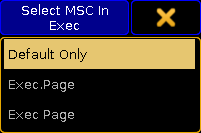
Select MSC (In) Exec pop-up
There are three options here:- Default Only - This option will make the MSC commands go to and from the selected executors on the Master station only.
- Exec.Page - This option can be used if the commands should be sent to a specific executor. The page and executor number needs to be separated by a dot (Hex = 2E).
- Exec Page - This option can be used if the commands should be sent to a specific executor. The page and executor number needs to be separated by a space (Hex = 20).
- Command:
Tapping here opens the Select MSC Command pop-up: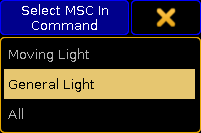
Select MSC (In) Command pop-up
There are three options here:- Moving Light - This option will select moving light command format (hex 02).
- General Light - This option will select the general lights command format (hex 01).
- All - This will use the all type format (hex 7F).
The button in the fourth row is called Send to. Tapping it open a Select Send to pop-up like this:
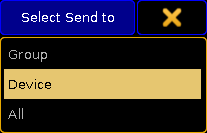
There are three options:
- Group:
Selecting this will make the station transmit MSC to the specified group number (1 to 15). - Device:
Selecting this will make the station transmit MSC to the specific device number (0 to 111). - All:
This option will transmit the the MSC to all connected devices.
The MSC Concept
The MSC command structure and syntax is based on the general SysEx structure defined by MMA (MIDI Manufacturers Association). It was released in 1991 as an extension to the general MIDI.
The raw MIDI information is written in hex octets (two hexadecimal numbers). Different software manufacturers might present the MSC in an interpreted way and show the data in a more human readable form. This can of course be nice, but since we cannot describe every way this can be presented, this manual is looking at the raw data.
The message format looks like this:
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
- F0 7F is the header that identifies the message as "universal system exclusive" and a "real time" message.
- Device ID is the device or group number.
- 02 is a hex octet specifying that the message is MSC.
- Command Format is an octet that specifies the equipment type.
- Command is an octet that defines the command type
- Data is the actual data. This might change depending on the command type.
- F7 is a closing octet finishing the message.
Device ID
The device ID is an octet actually divided into three different sections:
- 00 to 6F:
This is the 112 different specific devices that can be identified. - 70 to 7E:
This is the 15 group numbers. - 7F:
This is a broadcast ID that all devices listen to.
In grandMA2 the device ID and group ID can be set for both incoming and outgoing messages.
For transmitting MSC it can only transmit one octet in the Device ID location. The Send to setting (described above) selects which one of the three different sections Id that should be transmitted.
Command Format
The command format octet denotes the type of equipment that should receive the message (or at least respond). grandMA2 only transmit and respond to three different formats:
- 01:
This is the General Lighting format - 02:
This is Moving Lights format. - 7F:
This is an All format that all equipment should respond to.
Command
The command octet denotes the type of command in the message. The command type will dictate the data information.
grandMA2 supports 7 different command types:
- 01 (Go):
This is the same as a Goto command in grandMA2. It needs to be followed by a cue number. - 02 (Stop):
This is the same as a Pause command in grandMA2. This can be followed by a cue number. - 03 (Resume):
This will "un-plause" a cue. If a specific cue has been paused, then the cue number needs to be specified with this command. - 04 (Timed_Go):
This can be used to perform a Goto with a specific fade time. It needs both the time and the cue number - in that order. - 06 (Set):
Set can be used to set the position of faders. It needs the fader number and page followed by the position. - 07 (Fire):
This can be used to trigger macros. The macro number needs to follow the command. Only macro 1 to 255 can be triggered. - 0B (Go_Off):
This command can be used "Off" executors. This needs to followed by a cue number.
Data
01 (Go):
As stated above: This is interpreted as a GOTO command. A cue number needs to be specified. The cue number also needs to be transmitted in hex octets and the complete cue number including the decimals needs to be transmitted. If cue number 4 is to be triggered then the complete number is 4.000 - the number with all decimal numbers separated by a dot (Hex value 2E). Decimal numbers in hex is some of the easiest to convert. It needs a "3" in front. This means that decimal 4 becomes 34 in hex. The complete cue number including the dot is then: 34 2E 30 30 30.
See this table for a complete decimal to hex translation.
If the station is set to Default Only in the Send MSC In Exec option, then this all that needs to be added after the command.
Example: Triggering cue number 21.5 on the default executor (All Devices, All Format, and Default Only setting):
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 01 | 32 31 2E 35 30 30 | F7 |
If the setting is not Default Only, then an executor and page needs to be specified. There are two options for separating the executor number and the page number. It can be separated by a dot (hex = 2E) or by a space (hex = 20). The cue number and the executor/page data needs to be separated by a hex value 00.
Example: Triggering cue number 37.2 on executor 5 on page 1 (All Devices, All Format, and Exec.Page setting):
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 01 | 33 37 2E 32 30 30 00 35 2E 31 | F7 |
Same example but with a space separated executor and page:
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 01 | 33 37 2E 32 30 30 00 35 20 31 | F7 |
02 (Stop):
This is like hitting the pause button. Please read the section above for a better understanding of the hex cue numbering system.
With the Default Only option there does not need to be any extra data since it is the executor that is paused.
Example: Stopping the default executor (All Devices, All Format, and Default Only setting):
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 02 | F7 |
If the station is transmitting MSC, then it will transmit a cue number 0.000. This is like sending a “pause running cue” command.
If the settings are not Default Only but one of the two Exec/Page options, then the cue 0 also needs to be transmitted.
Example: Stopping executor 5 on page 1 (All Devices, All Format, and Exec.Page setting):
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 02 | 30 2E 30 30 30 00 35 2E 31 | F7 |
03 (Resume):
This is the only way to continue a paused cue. The only difference between the Stop and Resume commands are the “02” and “03”.
Example: Continuing the fade paused above (All Devices, All Format, and Exec.Page setting):
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 03 | 30 2E 30 30 30 00 35 2E 31 | F7 |
If the Default Only setting is chosen then the command is F0 7F 7F 02 7F 03 F7 to continue the fade.
04 (Timed_Go):
This is the same as the 01 (Go) command but with a specified time. Please read (and understand) about the 01 (GO) command and data above. Just to make this a bit simpler we are going to pretend that the “Default Only” option is turned on in the MSC options in Setup.
To transmit a timed Goto the time needs to be specified first and then the cue number. The time is specified by five hex octets. They represent (in order) Hour, Minute, Second, Frame, and Fraction.
The hour, minute, and second sections are very strait forward. The number needs to be transmitted in hex numbers. It is possible to transmit a value above the normal limit for example 64 seconds (hex = 40). The station will transmit this as 1 minute and 4 seconds.
Right now the console will not accept any time specified in the Frame and Fraction sections. But it transmit values below a second in the Frame section. The console divides the second into 24 frames. So 0.5 seconds is 12 Frames and the received hex number would be 0C.
Example: Goto cue 75 with the fade time of 20 seconds (All Devices, All Format, and Default Only setting):
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 04 | 00 00 14 00 00 37 35 2E 30 30 30 | F7 |
Example: Goto cue 5.4 with the fade time of 1 minute on executor 3 on page 1 (All Devices, All Format, and Exec.Page setting):
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 04 | 00 01 00 00 00 35 2E 34 30 30 00 33 2E 31 | F7 |
06 (Set):
The set command is used to move a fader to specific position. The 06 command is followed by two hex octets that indicates the fader and then two more octets that dictates the position.
The first of the two numbers for the fader is the fader number (on a page). The fader number 1 is hex number 00, the second is 01 and so on. Remember that this is a hex number so fader 16 have hex number 0F and decimal 17 is hex 10.
The second of the two numbers for the faders are the page number. This is a little different page 1 is hex number 01and page 2 is hex 02 and so on.
So executor 1 on page 1 is 00 01.
Calculating the position in hex numbers is a bit more tricky. The faders position is defined by a coarse and fine value. The scale for both values is 128 steps (most MIDI is in 128 steps). The fine value is transmitted first followed by the coarse value.
The desired fader position (in decimal) need to be multiplied by 1.28. The resulting integer is the coarse value. The remainder (everything on the right side of the separator) should be multiplied by 128 to get the fine value. The two decimal numbers then needs to be converted to hex.
Example:
The fader 3 on page 2 needs to be moved to 45%. First convert the position.
- Multiply 45 by 1.28 = 57.6
- Coarse value is 57.
- Multiply 0.6 by 128 = 76.8
- Fine value is 76.
- Convert decimal 57 to hex = 39.
- Convert decimal 76 to hex = 4C.
- Fine is transmitted before coarse so the position is: 4C 39
The MSC message is (All Devices and All Format setting):
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 06 | 02 02 4C 39 | F7 |
A fade time can be added after the fader and position data. The time format explained in the 04 command is used.
Example: Moving fader 15 on page 1 to 100% in 5 seconds (All Devices and All Format setting):
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 06 | 0E 01 7F 7F 00 00 05 00 00 | F7 |
The console only transmit the position of some faders - executors with sequences and all the green colored special masters (for the selected executor), but it accepts positions for all faders that have something assigned.
07 (Fire):
Macros can be fired by this command. It needs to be followed by a single octet specifying the macro number.
Macro number 1 is hex number 01. Hex number FF is macro number 255.
Example: Triggering macro number 64 (All Devices and All Format setting):
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 07 | 40 | F7 |
0B (Go_Off):
Executors can be turned off using the 0B command. A cue number needs to be transmitted - cue 0 can be used.
Example: Send an Off command to executor 9 on page 5 (All Devices, All Format, and Exec.Page setting):
| F0 7F | Device ID | 02 | Command Format | Command | Data | F7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 7F | 7F | 02 | 7F | 0B | 30 2E 30 30 30 00 39 2E 35 | F7 |
MIDI via Ethernet
MSC can sent using Ethernet. It is transmitted as a UDP message.
The MSC message is the same as described above, but the MSC message needs a header for the date to be accepted by the grandMA2.
The header separated into two parts. The first is identifying the message as a grandMA2 MSC message: 47 4D 41 00 4D 53 43 00 - it translates to GMA MSC.
The second part is four octets describing the length of the message - including the header. It is written as little endian byte format (least significant first).
This is calculated by counting the number of octets and then convert the decimal number into hex. Usually we only needs the first octet (it allows for messages up to 255 octets) although all four needs to be sent.
Examples:
Send a go command to cue 35. The MSC message is: F0 7F 7F 02 7F 01 33 35 2E 30 30 30 F7.
This is 13 octets. The header is always 12 octets. So the combined length is 25 octets. Decimal 25 is 18 in hex. The entire message is:
47 4D 41 00 4D 53 43 00 18 00 00 00 F0 7F 7F 02 7F 01 33 35 2E 30 30 30 F7
Trigger macro 1 is: F0 7F 7F 02 7F 07 01 F7 - 8 octets.
Plus the 12 from the header is decimal 20 = 13 hex.
The message is:
47 4D 41 00 4D 53 43 00 13 00 00 00 F0 7F 7F 02 7F 07 01 F7