- grandMA2 User Manual
- grandMA3 Mode2
- grandMA2 Quick Start Guide
- grandMA2 Quick Manual onPC solutions
- MA 3D
- MA VPU
- Introduction
- Help from MA technical support
- System requirements
- For your Safety
- Functions and Features
- Transition from grandMA video to MA VPU
- Teaser Mode
- Comparison VPU plus / VPU basic / VPU light
- Main Features
- Installation and Maintenance
- Startup
- Software update
- Service Packs
- Update of Fixture Types
- Backup
- Handling backups with the VPU
- Start Acronis on VPUs with serial Numbers up to # 86 on
- Start Acronis on VPUs with serial Numbers from # 87
- Restoring an image with Acronis
- Storing an image with Acronis
- Backup the VPU content after shipment
- Access VPU via Network
- Version of grandMA desk or grandMA onPC (off-line)
- IP Addresses
- IP Address of the PC
- Art-Net IP Address
- EDID Manager
- CITP / MSEX Protocol
- Installation and Maintenance
- Communication with the grandMA Desk Series
- Connection with the grandMA desk
- Connection with the grandMA onPC (off-line) software
- Connection States
- Data Management
- Master slave
- Principle function diagram
- Layer Properties
- Layer Reference
- Virtual Outputs
- Virtual Output: Configuration of a TripleHead2Go Digital Port
- Predefined Constellation
- Several MA VPU applications in one grandMA show
- Quickstart with grandMA2
- Program surface
- Internal Touch-Screen VPU plus
- Internal Screen VPU light
- Menu Bar
- File...
- View...
- Render...
- Help...
- Toolbar
- Status Bar
- Preview
- Multi Preview
- Content Editor
- Content: Image Pool (I-Pool)
- Content: Text Ticker
- Content: Eff1 Type...Eff4 Type
- Content: 3D Objects
- Content: Mask
- Warper
- Warper Fullscreen View
- Warper Basic Operation
- Warping
- File Browser
- Features Attributes and Functions
- Order of Effect Execution
- Softedging
- Keystoning
- Pixel Mapper
- VPU - Pixel Mapper Graphical View
- Pixel Mapper Toolbar
- Pixel Mapper Editor
- VPU - Pixel Mapper Grid View
- Console - VPU Pixel Mapper View
- VPU - Pixel Mapper Graphical View
- Creation of customized 3D Objects
- Content Specifications
- Rovi Total CodeStudio for converting your content into MPEG2
- Hap Content Converter
- Warnings
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- FAQ and Troubleshooting
- Supplement MA Lighting
- Intended use
- Data
- Symbols and warning labels
- LIMITATIONS
- Transport
- General Safety Instructions
- IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
- Electric shock warning on the rear of the grandMA
- Safety and Environment
- Quickstart Connect VPU plus
- Quickstart Connect VPU light
- Switching the apparatus On/Off
- Maintenance
- Conformity
- Introduction
- Release Notes
Version 3.9
Features Attributes and Functions
To explain the layer effect engine it is illustrative to imagine grandMA VPU as a model of a several movable cameras where every camera looks at a layer object like a 2D plane or a 3D cube.
In these examples an image may be a texture (picture), or a video.
| Layer Features and Attributes | Example | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| with values in % | ||||
| Dimmer | Dimmer 50 % | Dimmer 100 % | ||
| Dimmer function. To facilitate fading between different layers the dimmer controls the transparency of an object. If the dimmer is 0 the object is transparent and the projection is invisible. If the dimmer is “full” the object is opaque and you can only see the front layer (front Z-position) |
 |
 |
||
| MixColor (R; G; B) | Color (0,0,0) | Color(100,100,0) | ||
| Tint the output with the RGB (Red; Green; Blue)color mixer |  |
 |
||
| HSBC (Hue shift, Saturation, Brightness + Contrast) | HSBC (50,50,50,50) |
|
||
| Set Hue, Saturation and Brightness of a layer |  |
 |
||
| Colorkey | Layer 2 Key R,G,B (100,0,0) Tol (10) |
|||
| Image Layer 1 | Image Layer 2 | |||
| Set the transparency for the foreground object. |  |
 |
||
| First select the color then set the tolerance. | Resulting Output Image | |||
| The switch 'Alpha’ decides if the pixel gets complete transparent or opaque in dependency to the color key. |  |
|||
| The switch 'Type’ decides if the calculation is done in the RGB (Red Green Blue) or HSB (Hue Saturation Brightness) model. | ||||
| Colorboost (ColBoost-R; -G; -B) | ColBoost (50,50,50) | ColBoost (50,50,100) | ||
| Manipulate the intensity of red, green or blue color of the image separately. |  |
 |
||
| Borders | ||||
| soft Borders | hard Borders | |||
| (Left Hard, Left Soft, Right Hard…Top Hard, Top Soft) Borders can be used for realizing PiP (picture in picture) applications. Softborder works with alpha channels so that the layer underneath can even shine through the top layer to merge the layers. For example first cut the layer to a smaller size (which is NOT scaling!) and then create a soft edge by using the soft parameter for the respective side of the layer. This makes the layer underneath shine through (see picture). Borders also can be changed via the special dialog in the desk: Therefore select the layer, select the feature 'Border' and press the button 'Special Dialog' at the desk. |
 |
 |
||
| VObj. (3D-Objects) | cross | sphere | ||
| Select an 2D or 3D object on which surface the image or video is shown |  |
 |
||
| VObj (Transistion Type) | ||||
| Single Layer Transistion Note: (grandMA 2 only) Select a fade effect between images on the layer. |
 |
 |
||
| VObj (Transistion Time) | ||||
| The transistion time can be set from 0….3600 seconds | ||||
| VObj. I-Pool | Pool ‚Standard’ selected | Pool ‚Video Test2’ selected | ||
| Selection of the 'I-Pool’. One ‚Pool’ can contain up to 255 images or videos | 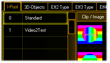 |
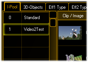 |
||
| VObj. Images | Image 1 | Image 2 | ||
| Choose the image or video from the selected 'Pool’ |  |
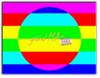 |
||
| VPos (X; Y; Z ; Scale) | X= 50%; Y=50%; Z=50% | X=25%; Y=25%; Z=25% | ||
| Scale modifies the range of X ;Y ;Z | ||||
| Positioning of the projection object in X; Y; Z - direction |  |
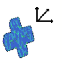 |
||
| VRot (X; Y; Z) | X=40%; Y=60%; Z=50% | X=40%; Y=40%; Z=40% | ||
| Rotate the projection object around the X; Y; and Z-axis | 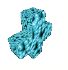 |
 |
||
| VPos <> (X; Y;Z) | X=50%; Y=50%; Z=50% | X= 60%; Y=60%; Z=50% | ||
| Animate continuous moving of the projection object in X; Y and Z - direction |  |
 |
||
| VRot<> (X; Y;Z) | X= 50%; Y=50%; Z=50% | X= 50%; Y=50%; Z=60% | ||
| Animate continuous rotation of the object around the X; Y and Z - axis | 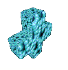 |
 |
||
| VScale (X; Y; Z) | X= 50%; Y=50%; Z=50% | X= 50%; Y=30%; Z=50% | ||
| Scale the dimensions of the object in X; Y ;Z direction |  |
 |
||
| VImg (Split X; Split Y) | Split X 0; Split Y 0 | Split X 2; Split Y 2 | ||
| Split the image or video in X and Y |  |
 |
||
| VImg (Offset X; Offset Y) | Offset X=0; Offset Y=0 | Offset X=50%; Offset Y=0% | ||
| Offset of the image or video |  |
 |
||
| VImg<> (X; Y) | X= 50%; Y=50% | X= 60%; y=50% | ||
| Animate continuous scrolling of the image or video on the object |  |
 |
||
| VPlayer (Playmode Speed; Begin; End; Index) | Frame 100 | Frame 200 | ||
| (Only for videos) | ||||
 Frame Index: Select a single frame with the Index channel Play: Starts the Video once forward from the beginning to the end Stop: Stops immediately Pause: Pauses Resume: Continues after Pause (even with the Looping) Play Index: Plays the video from the index frame which has to be set first |
 |
 |
||
| Loop: Starts the video endless looped forward from the beginning | 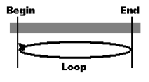 |
|||
| Loop Index: Loops around the frames index which has to be set first | 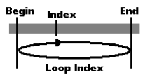 |
|||
 Play Ignore Dimmer;Loop Ignore Dimmer; Loop Index Ignore Dimmer; Play Index Ignore Dimmer; Pause Ignore Dimmer; These modes start/pause the video and keep on playing reguardless if the dimmer is on or zero |
||||
| VPlayer (Speed) modify the playback speed | ||||
| VPlayer (Begin) Set an inpoint | ||||
| VPlayer (End) Set an outpoint | ||||
| VPlayer (Index) Select a frame index | ||||
| VEffect 1…...4 (Eff Type; Eff part) | Eff Type = 0 | Eff Type = Sepia | ||
| Several effects based on the Direct3D standard can be selected. Effects are defined within .fx files as described in Content: Eff1 Type…Eff4 Type. |
 |
 |
||
| Sound (Volume) | SndVol = 0% | SndVol = 100% | ||
| Control the sound output for video files with a soundtrack | Sound is off | Sound is on | ||
| Master Features and Attributes | Example Fullscreen View | |
|---|---|---|
| Beam | ||
| Iris (Iris) | Iris = 10 % | Iris = 80 % |
| Open or close the Iris |  |
 |
| Control | ||
| Control (CTRL) | ||
| The Control channel of the Master Layer is used to switch to the Fullscreen View or to shut down the VPU via the desk. These functions are available as buttons in the Smart View: - No Operation: --- - Shutdown: Shutdown VPU - Restart: Restart VPU - Fullscreen: Fullscreen Mode - Windowed: Windowed Mode - Enter PM: Start Pixel Mapper - Leave PM: Leave Pixel Mapper - Enter SMode: Enters the Show Mode - Leave SMode: Leaves the Show Mode |
 |
 |
| Shapers | ||
| Shaper (1A; 1B; 2A; 2B; 3A; 3B; 4A; 4B) | 1A=0; 1B=0; 2A=0; 2B=0; 3A=0; 3B=0; 4A=0; 4B=0 % | 1A=30; 1B=0; 2A=30; 2B=0; 3A=30; 3B=0; 4A=30; 4B=0 % |
| With the beam shapers the resulting image can be masked variable with four shapers each with 2 channels A and B. With the Blade switch shapers can be switched on or off. |
 |
 |
| Video | ||
| VObj (Image) | Image = no Image | Image = Circle |
| Select the image for the iris mask |  |
 |
*As described in Eff1 Type…Eff4 Type
Hint:
Camera effects manipulate the complete output signal!
Camera effects manipulate the complete output signal!
| Camera Features and Attributes | Example with values in % | |
|---|---|---|
| Color | ||
| HSBC (Hue shift, Saturation, Brightness + Contrast) | HSBC (50,50,50,50) | HSBC (50,0,50,50) |
| Set Hue, Saturation, Brightness and Contrastof a layer |  |
 |
| Colorboost (ColBoost-R; -G; -B) | ColBoost (50,50,50) | ColBoost (50,50,100) |
| Manipulate the intensity of red, green or blue color of the image seperately. |  |
 |
| Beam | ||
| Iris (Iris) | Iris = 10 % | Iris = 80 % |
| Open or close the Iris |  |
 |
| Shapers | ||
| Shaper1 (1A; 1B; 2A; 2B; 3A; 3B; 4A; 4B) | 1A=0; 1B=0; 2A=0; 2B=0; 3A=0; 3B=0; 4A=0; 4B=0 % | 1A=30; 1B=0; 2A=30; 2B=0; 3A=30; 3B=0; 4A=30; 4B=0 % |
| With the beam shapers the resulting image can be masked variable with four shapers each with 2 channels A and B. |  |
 |
| Video | ||
| VObj (Images) | Image = no Image | Image = Circle |
| Select the omage for the iris mask |  |
 |
| VScale (X; Y; Z; All) | X= 50%; Y=50%; Z=50% | X= 50%; Y=30%; Z=50% |
| Scale the dimensions of the object in X; Y ;Z direction |  |
 |
| VImg (Split X; Y Offset X; Y) | Split X 0; Split Y 0 | Split X 2; Split Y 2 |
| Split the image in X and Y. Split offset of the image. | ||
| This offset can be understood as the Point of View (PoV). By using this function the perspective doesn´t change. Try this with the cube and you will clearly see the difference! |
 |
|
| VCamPos (X; Y; Z) | X=50%;Y=50%;Z=50% | X=46%;Y=52%;Z=54% |
| All layer views are mixed up to one view for the main cameras whose images are send to the physical outputs. These imaginary cameras can be moved to show only parts of the whole image. So several applications can be connected together to project a huge image. If the camera position moves the perspective changes: Take a cube, rotate it a bit and then move the camera. You can see that the perspective changes - you can see that the „world´s“center is still the centre of your monitor. |
 |
 |
| VCamRot (X; Y; Z) | ||
| Rotate the camera around its own centerpoint | ||
| VEffect 1…...4 (Eff Type; Eff part) | Eff Type = 0 | Eff Type = Sepia |
| Several effects based on the Direct3D standard can be selected. Effects are defined within .fx files as described in Content: Eff1 Type…Eff4 Type. |
 |
 |
| 3D Key (PosX;Y;Z Rot X;Y;Z Scale X;Y;Z; All) | ||
| Select a 3D object for the camera. This is useful to manipulate the complete output e.g. for projecting on a cyclorama or display all layers on a sphere. |
||
| Keystone (1A,; 1B; 2A; 2B; 3A; 3B; 4A; 4B) | 1A=0; 1B=0; 2A=0; 2B=0; 3A=0; 3B=0; 4A=0; 4B=0 % | 1A=0; 1B=0; 2A=0; 2B=30; 3A=0; 3B=0; 4A=0; 4B=30 % |
| All layer views are mixed up to one view for the main camera. Each edge of this view can be moved towards the opposite edge to generate a keystone effect. |
 |
 |
| Keystone Corr. (X - Corr.; Y - Corr.) | X Corr. = 0 %; Y Corr. = 0 % | X Corr. = 75 %; Y Corr. = 0 % |
| If a picture is projected distorted on a surface, a perspective correction is necessary to distribute the content on the surface correctly. Therefore the distribution of the picture content can be manipulated in X- and Y-direction. |
 |
 |
| Softedge (1A,; 1B; 2A; 2B; 3A; 3B; 4A; 4B) | 1A=0; 1B=0; 2A=0; 2B=0; 3A=0; 3B=0; 4A=0; 4B=0 % | 1A=0; 1B=0; 2A=50; 2B=0; 3A=0; 3B=0; 4A=0; 4B=0 % |
| If several projectors should show one common image, the borders must be cross faded. For every border one channel for the position and one channel for the dispensation of the black wedge exist. This example shows a soft edging for the left border of the image. |
 |
 |
| Splitscreen (Offset X; Offset Y) | ||
| Changing the X or Y offset doesn't change the point of view. Camera axis stays on the object axis. This is different from VCamPos. |
||
| CP-X, CP-Y, CP-Z | ||
| Rotate the camera around the center point of the 3D-world | ||
| FOV | ||
| Change the field of view of the camera. |