- grandMA2 User Manual
- grandMA3 Mode2
- grandMA2 Quick Start Guide
- grandMA2 Quick Manual onPC solutions
- MA 3D
- Help from MA technical support
- Symbols used
- Introduction
- Install and Uninstall
- System Requirements
- Installation
- Uninstall MA 3D
- First Steps
- Hardware connection
- Start MA 3D
- Create a Session
- Data Management
- Master/Slave
- Coordinate system
- Program Surface
- Menu Bar
- Menu Bar - File Menu
- Settings
- Edit
- Functions
- Tools
- View
- Help
- Tool Bar
- Main Windows
- Stage View
- Mouse + Keyboard Actions
- Arrangement of Objects (Align Objects)
- Duplicate (copy 3D Objects)
- 3D Objects
- Assets (Information Window)
- Properties
- Media Database
- Materials
- Video Player
- Moving Paths
- Sessions
- Status Bar
- Windows Layout
- Menu Bar
- Fixture Types
- 3D Modeling and Import
- Workflow
- 3D Modeling Principles
- Creation of a 3D Model
- Creation of a 3D Fixture Model
- Import 3D Model to MA 3D
- Assigning of 3D Models to Fixture Types
- Checklist for 3D Modeling
- Automated import
- Parameters
- Axes
- Rotation Axes
- Linear Axes
- Beam of Light (Cone)
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- MA 3D FAQ
- MA VPU
- Release Notes
Version 3.9
Creation of a 3D Model
3D objects can be created with 3D CAD programs. The amount of polygons affects the performance because for each polygon the projection has to be calculated. The lesser the number of polygons, the better the frame rate.
MA 3D supports the following formats for 3D objects:
• .3ds - Format for drawing 3 dimensional objects
Important:
- The orientation of the object has to fit
- Normals have to be organized correctly
- UV coordinates for the textures have to be setup correctly
This example shows the creation of a halved cylinder created with Cinema 4D:
 |
Insert an object of type 'Cylinder’. | ||||||||
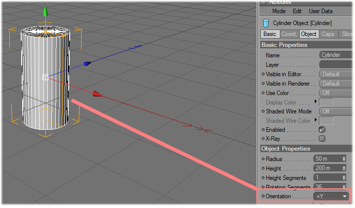 |
Set the orientation to "+Y".
For the correct orientation of the object in MA 3D, it is important to set the correct orientation in Cinema 4D. |
||||||||
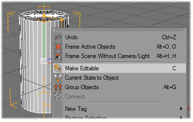 |
Make the object editable. | ||||||||
 |
Select polygons that are not used. | ||||||||
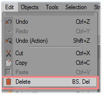 |
Delete them. | ||||||||
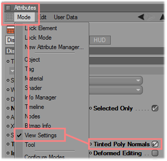 |
Set the option "Tinted Poly Normals" to On in the "View Settings". | ||||||||
|
|
The next copy steps are only necessary if the object has to be visible from both sides. The object has to be duplicated and the normals have to be set in both directions. First copy the object. | ||||||||
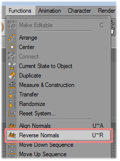 |
Then reverse the normals of the copy. | ||||||||
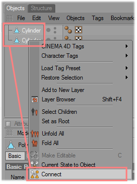 |
Select both cylinder objects and connect them to a new cylinder. | ||||||||
 |
The old cylinder objects can be deleted. | ||||||||
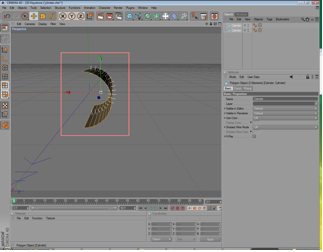 |
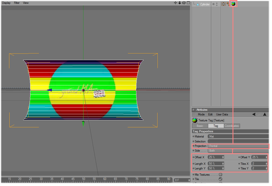
Now you can see two objects with normals in both directions. | ||||||||
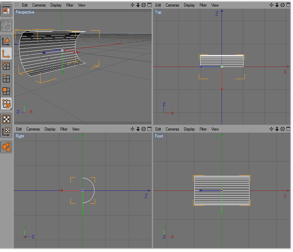 |
Check the orientation of the resulting object. | ||||||||
 |
Insert a new material for the texturing. | ||||||||
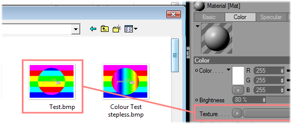 |
Assign an image to the texture and the material to the object (Mind the restriction of max. 8 characters + extension for the image name!). | ||||||||
|
|
Adjust the texture mapping parameter. | ||||||||
 |
Assign the UV coordinates for the texture mapping. | ||||||||
|
|
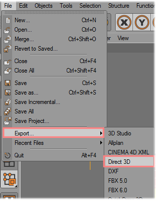
Export the object to 3D Studio format (.3ds). Objects created in this way can be added via the import tool. | ||||||||
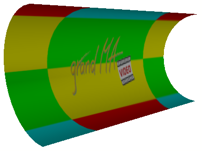 |
The result. |